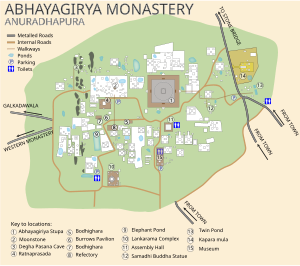
Abhayagiri Vihāra
Abhayagiri Vihāra was a monastery in the ancient Sri Lankan city of Anurādhapura and also the name of the fraternity of Buddhist monks associated with the monastery. The Abhayagiri Vihāra tradition was one of three sects of Buddhist monks that existed for a period in ancient Sri Lanka, the other two being the Jetavana Vihāra and the Anurādhapura Mahāvihāra.[1]
The Abhayagiri Vihāra was founded in the 2nd century BC; it had grown into major institution by the 1st century AD.[2]
Approaching the Buddhist Path states:
- Chinese pilgrims recorded that Abhayagiri, the largest and wealthiest monastery, followed both the early scriptures and the Mahayana scriptures; some of the Mahayana sutras in the Chinese Tripitaka were obtained in Sri Lanka. There are also many bodhisattva statues and Mahayana art on the island, and there is evidence that some Tantric teachings were present there as well.[3]
The Abhayagiri Vihara tradition came to an end during the reign of King Parakkamabāhu I (1153–1186 CE), who decreed that rival Anurādhapura Mahāvihāra was the only legitimate tradition in Sri Lanka. The king deligitimized the Abhayagiri and Jetavana traditions, and forced the monks from these traditions to give up their vows or follow the Anurādhapura Mahāvihāra.
The Abhayagiri Dagaba (stupa) was fully restored and renovated by the Sri Lankan Central Cultural Fund as a UNESCO project. It was unveiled in June 2015.[4]
Notes
- ↑ Warder 2000, p. 280.
- ↑
 Abhayagiri Vihāra, Wikipedia
Abhayagiri Vihāra, Wikipedia
- ↑ Dalai Lama & Thubten Chodron 2017, Chapter 1.
- ↑ "Abhayagiri Stupa to be unveiled » the Nation". Archived from the original on 7 August 2016. Retrieved 4 May 2016.
Sources
 Dalai Lama; Thubten Chodron (2017), Approaching the Buddhist Path, The Library of Wisdom and Compassion, Volume 1, Wisdom Publications
Dalai Lama; Thubten Chodron (2017), Approaching the Buddhist Path, The Library of Wisdom and Compassion, Volume 1, Wisdom Publications Warder, A.K. (2000), Indian Buddhism (Third ed.), Dheli: Motilal Banarsidass
Warder, A.K. (2000), Indian Buddhism (Third ed.), Dheli: Motilal Banarsidass
Further reading
 Abhayagiri Vihāra, Wikipedia
Abhayagiri Vihāra, Wikipedia- Hirakawa, Akira; Groner, Paul (2007). A History of Indian Buddhism: From Śākyamuni to Early Mahāyāna. Motilal Banarsidass. hdl:10125/23030. ISBN 978-8120809550.
- Sujato, Bhikkhu (2006), Sects and Sectarianism, Santi Forest Monastery
- von Schroeder, Ulrich. (1990). Buddhist Sculptures of Sri Lanka. (752 p.; 1620 illustrations). Hong Kong: Visual Dharma Publications, Ltd. ISBN 962-7049-05-0
- von Schroeder, Ulrich. (1992). The Golden Age of Sculpture in Sri Lanka – Masterpieces of Buddhist and Hindu Bronzes from Museums in Sri Lanka, [catalogue of the exhibition held at the Arthur M. Sackler Gallery, Washington, D. C., 1 November 1992 – 26 September 1993]. Hong Kong: Visual Dharma Publications, Ltd. ISBN 962-7049-06-9
External links
 Media related to Abhayagiri Monastery (Anuradhapura) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Abhayagiri Monastery (Anuradhapura) at Wikimedia Commons- Discover Sri Lanka – More information & images about Abhayagiri Dagaba
| This article includes content from Abhayagiri Vihāra on Wikipedia (view authors). License under CC BY-SA 3.0. |