Greco-Buddhism
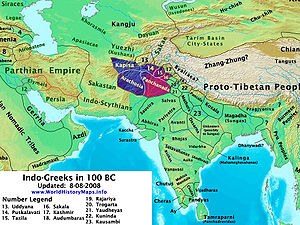
Greco-Buddhism, or Graeco-Buddhism, is the cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism, which developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Bactria and the Indian subcontinent, corresponding to the territories of modern-day Afghanistan, Tajikistan, India, and Pakistan. It was a cultural consequence of a long chain of interactions begun by Greek forays into India from the time of Alexander the Great. The Macedonian satraps were then conquered by the Mauryan Empire, under the reign of Chandragupta Maurya. The Mauryan Emperor Ashoka would convert to Buddhism and spread the religious philosophy throughout his domain, as recorded in the Edicts of Ashoka. Following the collapse of the Mauryan Empire, Greco-Buddhism continued to flourish under the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Greek Kingdoms, and Kushan Empire. Buddhism was adopted in Central and Northeastern Asia from the 1st century AD, ultimately spreading to China, Korea, Japan, Siberia, and Vietnam.
- Further reading
 Greco-Buddhism, Wikipedia
Greco-Buddhism, Wikipedia
| This article includes content from Greco-Buddhism on Wikipedia (view authors). License under CC BY-SA 3.0. |