Twenty-four non-concurrent formations
Twenty-four formations not concurrent with mind (Skt. citta-viprayukta-saṃskāra; T. ldan min 'du byed nyi shu bzhi ལྡན་མིན་འདུ་བྱེད་ཉི་ཤུ་བཞི་) are identified in the Gateway to Knowledge (GTK). The Abhidharma-samuccaya (ADS) combines the first two factors (prāpti and aprāpti) for a total of twenty three factors.
According to the Gateway to Knowledge, these lists are not exclusive. The actual number of non-concurrent formations is beyond counting.[1]
This first set of fourteen factors are listed in both the Abhidharma-kosa and the Abhidharma-samuccaya (ADS), though the ADS combines the first two factors in this set (as prāpti).
- 1. prāpti (T. thob pa) - possession
- 2. aprāpti (T. ma thob pa) - dispossession
- 3. sabhāgatā (T. skal mnyam / ris mthun) - homogeneity, same status or similar class
- 4. asaṃjñāsamāpatti (T. 'du shes med pa'i snyoms 'jug) - meditative attainment of non-discernment
- 5. asaṃjñika (T. 'du shes med pa) - state of non-discernment
- 6. nirodhasāmapatti (T. 'gog pa'i snyoms 'jug) - meditative attainment of cessation
- 7. jīvitendriya (T. srog gi dbang po) - life-force
- 8-11. four characteristics of conditioned phenomena
- 12-14. nouns, phrases and letters
The remaining ten factors are listed in the Abhidharma-samuccaya, but are not found in the Abhidharma-kosa.[1]
- pṛthagjanatva (T. སོ་སོའི་སྐྱེ་བོ་ ) - ordinary person (GTK), status of an ordinary man (ADS)
- pravṛtti (T. འཇུག་པ་) - continuity (OA), regular sequence (GTK)
- pratiniyama (T. སོ་སོར་ངེས་པ་) - distinction (OA), definitive distinctiveness (GTK), diverse regularity (ADS)
- yoga (T. འབྱོར་འབྲེལ་བ་) - union (OA), connected link (GTK)
- java (T. མགྱོགས་པ་) - rapidity (OA), speed (GTK)
- anukrama (T. གོ་རིམ་) - sequence (OA, GTK), gradation (ADS)
- kāla (T. དུས་) - time
- deśa (T. ཡུལ་)- location (OA, GTK), orientation
- saṃkhyā (T. གྲངས་) - enumeration (OA), number (GTK, ADS)
- sāmagrī (T. ཚོགས་པ་) - assembly (OA), gathering (GTK)
Note that Ornament of Abhidharma (OA) and Science and Philosophy in the Indian Buddhist Classics identify only nine additional factors from the Abhidharma-samuccaya; these texts omit pṛthagjanatva.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mipham Rinpoche 2004, s.v. Formations.
- ↑ Thupten Jinpa 2017, s.v. Non-associated formative factors.
Sources
 Asanga (2001), Abhidharmasamuccaya: The Compendium of the Higher Teaching (Philosophy), translated by Boin-Webb, Sara; Rahula, Walpola, Asian Humanities Press
Asanga (2001), Abhidharmasamuccaya: The Compendium of the Higher Teaching (Philosophy), translated by Boin-Webb, Sara; Rahula, Walpola, Asian Humanities Press Buswell, Robert E.; Lopez, Donald S. (2014), The Princeton Dictionary of Buddhism, Princeton University
Buswell, Robert E.; Lopez, Donald S. (2014), The Princeton Dictionary of Buddhism, Princeton University Chim Jampaiyang (2019), Jinpa, Thupten, ed., Ornament of Abhidharma: A Commentary on Vasubandhu's Abhidharmakosa, translated by Coghlan, Ian James (Apple Books ed.), Library of Tibetan Classics
Chim Jampaiyang (2019), Jinpa, Thupten, ed., Ornament of Abhidharma: A Commentary on Vasubandhu's Abhidharmakosa, translated by Coghlan, Ian James (Apple Books ed.), Library of Tibetan Classics Mipham Rinpoche (2004), Gateway to Knowledge, vol. I, translated by Kunsang, Erik Pema, Rangjung Yeshe Publications
Mipham Rinpoche (2004), Gateway to Knowledge, vol. I, translated by Kunsang, Erik Pema, Rangjung Yeshe Publications Thupten Jinpa, ed. (2017), Science and Philosophy in the Indian Buddhist Classics, Volume 1: The Physical World, translated by Coghlan, Ian James, Wisdom Publications
Thupten Jinpa, ed. (2017), Science and Philosophy in the Indian Buddhist Classics, Volume 1: The Physical World, translated by Coghlan, Ian James, Wisdom Publications
External links
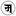 ldan_min_'du_byed_bcu_bzhi, Rangjung Yeshe Wiki
ldan_min_'du_byed_bcu_bzhi, Rangjung Yeshe Wiki